Artificial intelligence startup xAI, founded by Elon Musk, has shared a major new development plan with city and county officials in Memphis. Last week, the company announced that it intends to build a small solar farm directly beside its Colossus data center, one of the world’s largest facilities dedicated to training advanced AI models.
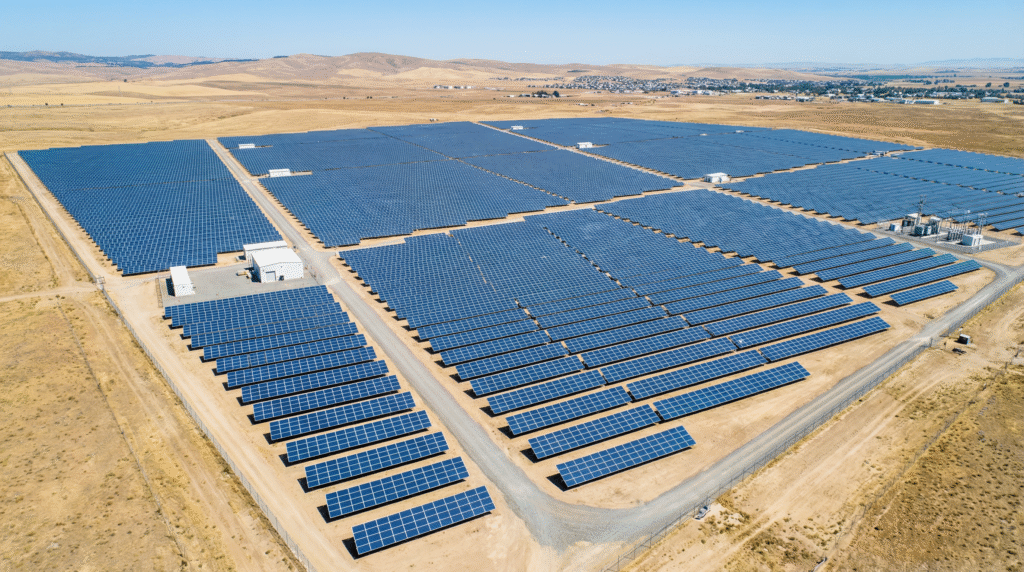
A New Solar Project Adjacent to Colossus
xAI Solar Farm Colossus Data Center. According to the proposal, the solar project will spread across 88 acres located to the west and south of the data center. These plots lie next to a 136-acre vacant lot owned by the same developer that controls the Colossus site.
Based on its size, experts estimate that the solar farm could generate around 30 megawatts of electricity. However, this amount is only about 10% of the data center’s projected power needs. Even so, xAI says the project is a first step toward expanding clean energy capacity for its AI operations.
Environmental Concerns and Legal Challenges
Despite its renewable energy plans, xAI is facing growing criticism for running over 400 megawatt-hours of natural-gas turbines without the proper permits. The Southern Environmental Law Center (SELC), working in conjunction with the NAACP, alleges that the company has been operating at least 35 turbines capable of releasing over 2,000 tons of nitrogen oxide (NOx) pollution annually. NOx emissions are known to worsen smog and cause serious respiratory problems.
Residents of Boxtown, a predominantly Black neighborhood near the facility, have strongly opposed the turbines. A study from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, found that nitrogen dioxide levels increased by 79% in areas around the data center after xAI began operations. Community members also report rising cases of asthma and other breathing issues since the turbines were activated.
Local officials have given xAI a permit to operate 15 turbines through January 2027, but the company says it will continue using additional turbines until it secures more reliable power sources.

xAI’s Larger Renewable Energy Plan
In September, xAI announced a more ambitious project — a 100-megawatt solar farm paired with 100 megawatts of grid-scale batteries designed to supply power 24/7. This project received a significant federal boost:
- Seven States Power Corporation, the solar developer, secured $439 million from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- Out of this, $414 million is an interest-free loan, a notable exception at a time when many clean-energy grants have been canceled under the Trump administration’s policies.
Expansion to Mississippi
In addition to its operations in Tennessee, xAI has deployed more gas turbines in Mississippi to support Colossus 2, its second major data center. The site currently has 59 turbines, and the company considers 18 of them temporary, which means regulators do not track their emissions.
xAI, Elon Musk solar farm, Colossus data center, AI data centers, clean energy for AI, Memphis solar project, nitrogen oxide pollution, Boxtown community impact, renewable energy xAI, natural gas turbines xAI, solar power for AI models, environmental concerns xAI.
Here is a clean, well-structured ~600-word SEO article based on your topic and keyphrase xAI solar farm Colossus data center. It’s written to be RankMath-friendly, readable, and optimized for Google.
Musk’s xAI Plans 88-Acre Solar Farm Next to Massive Colossus Data Center: What It Means for the Future of AI
The race to build faster, more powerful artificial intelligence systems has opened a new front: energy. As AI models grow exponentially, so does the electricity required to train and operate them. With this challenge in mind, Elon Musk’s xAI is now planning an 88-acre solar farm next to its colossal Colossus data center, signaling a major move toward sustainable, self-powered AI computing. The project has quickly become a talking point across the tech world as analysts assess what this could mean for the future of AI infrastructure.
A Large-Scale Solar Investment for AI’s Energy Demands
The xAI solar farm Colossus data center plan is not just another clean-energy project. According to early documents and industry chatter, the 88-acre solar installation is designed to offset a significant portion of the energy consumption from xAI’s upcoming data center—one expected to house thousands of high-performance GPUs and next-generation AI accelerators.
Large language models (LLMs) like Grok, GPT, and other frontier AI systems require enormous electricity, especially during training cycles. By investing directly in renewable power, Musk’s xAI aims to reduce long-term operating costs, ensure a stable power supply, and demonstrate a forward-looking approach to energy resilience.
Why the Solar Farm Matters Right Now
Demand for AI infrastructure has skyrocketed in the last eighteen months. Cloud providers, startups, and enterprises all compete for limited GPU capacity, and power shortages have forced many companies to delay or relocate their data center plans. In this environment, xAI’s solar farm strategy delivers several key advantages:
1. Energy Independence
Data centers around the world struggle with grid limitations. By generating its own renewable electricity, xAI can keep scaling without waiting for utility expansions.
2. Lower Long-Term Costs
While the initial investment in an 88-acre solar farm is substantial, it significantly reduces electricity bills over time. This matters when AI clusters run power-hungry hardware 24/7.
3. Environmental Positioning
Clean energy is becoming a competitive advantage. Tech firms that can show real reductions in carbon impact attract more enterprise partnerships and friendlier regulation.
4. Future-Proofing Against Energy Regulations
As governments introduce stricter energy-use standards for data centers, solar-powered facilities will naturally meet compliance requirements.
How It Supports the Colossus Data Center
xAI’s Colossus data center is expected to be one of the largest AI-optimized facilities in the United States. With racks of cutting-edge chips designed to train increasingly complex models, its electricity needs will surpass many traditional data centers.
The new solar farm will likely connect directly to the Colossus facility through a private microgrid or power distribution system. While solar energy alone cannot fully power such a massive center—especially at night—it can significantly offset consumption and reduce reliance on local utilities. Additional battery storage or supplemental power generation may also be included in future expansions.
Industry Reactions and What Comes Next
Industry analysts view the xAI solar farm Colossus data center plan as a sign of where AI infrastructure is heading. Companies can no longer rely solely on traditional power grids. Instead, they must build hybrid energy ecosystems combining renewables, storage, and even new technologies like small-modular nuclear reactors.
Elon Musk has long been an advocate for solar energy through Tesla’s SolarCity and Powerwall projects, so this move aligns with his broader vision. If successful, the model could spread across Silicon Valley and beyond, influencing how future AI buildings are designed.
Final Thoughts
xAI’s 88-acre solar farm proposal highlights a turning point in the AI industry. As data centers become the engine rooms of global innovation, the power behind them matters more than ever. The combination of scale, sustainability, and independence puts Musk’s xAI in a strong position to lead the next era of AI development.

